Difference between revisions of "AND node"
(New page.) |
m (Changes per Dr. Lamb.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | An '''AND node''' is a [[node (in neurocognitive linguistics)|node]] in [[compact relational network | + | An '''AND node''' is a [[node (in neurocognitive linguistics)|node]] in [[compact relational network notation]]. It is represented by an isosceles triangle about half as tall as it is wide, with [[line|lines]] connecting to other nodes. The node can be oriented with the apex at top ("downward AND") or bottom ("upward AND"). One line connects to the apex and two or more lines to the opposite (long) side; those two or more lines represent a conjunctive relationship. The AND node shows combinations as opposed to alternations, which are shown by the [[OR node]]. |
| + | |||
AND nodes have two principal types: | AND nodes have two principal types: | ||
==== Ordered AND ==== | ==== Ordered AND ==== | ||
| − | The lines on the plural side | + | The lines on the plural side operate in sequence, left to right. This type of AND shows the relationship of concatenation. |
| + | [[Image:Orderand.jpg]] | ||
In this example, downward activation from A goes to B ''and later'' to C. Upward activation from B ''and later'' from C goes to A. | In this example, downward activation from A goes to B ''and later'' to C. Upward activation from B ''and later'' from C goes to A. | ||
Revision as of 04:54, 5 August 2008
An AND node is a node in compact relational network notation. It is represented by an isosceles triangle about half as tall as it is wide, with lines connecting to other nodes. The node can be oriented with the apex at top ("downward AND") or bottom ("upward AND"). One line connects to the apex and two or more lines to the opposite (long) side; those two or more lines represent a conjunctive relationship. The AND node shows combinations as opposed to alternations, which are shown by the OR node.
AND nodes have two principal types:
Ordered AND
The lines on the plural side operate in sequence, left to right. This type of AND shows the relationship of concatenation.
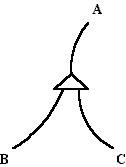 In this example, downward activation from A goes to B and later to C. Upward activation from B and later from C goes to A.
In this example, downward activation from A goes to B and later to C. Upward activation from B and later from C goes to A.
Unordered AND
A different type of combination in which the components are simultaneous. The multiple lines connect to the same point on the plural side of the triangle.
 In this example, downward activation travels through the line on the singular side, through the node, then down both lines on the plural side simultaneously. Upward activation travels up both plural-side lines simultaneously, then through the node and up the singular-side line.
In this example, downward activation travels through the line on the singular side, through the node, then down both lines on the plural side simultaneously. Upward activation travels up both plural-side lines simultaneously, then through the node and up the singular-side line.
The AND Node in Narrow Notation
(Description yet to be written.)
Sources
- LangBrain.
- Lamb, Sydney M., Pathways of the Brain: The Neurocognitive Basis of Language, John Benjamins, 1999.